how do we see color physics
A type of photoreceptor cell in the retina which helps us to see different colors. I am not at all an expert in the biophysics of the eye but my guess is the following.
The Physics Of Light And Color Light Filtration Olympus Ls
We can perceive colors in things like crayons and flowers since they reflect and absorb the rays of.

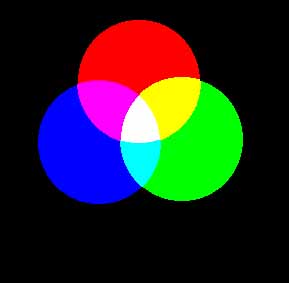
. Brown is a mixture of the different primary colors. Light in these colours can be added together to make the secondary colours magenta cyan and yellow. A blue object reflects blue light but absorbs all other waves.
How do we see colors physics. The violet line leads to three readings on the red green and blue cones. Light receptors are present in the eye which transmits the messages to the brain.
A type of photoreceptor cell in the retina which helps us to see in low light. The human brain and the human eye cooperatively translate light into color. Another 2 respond strongest to blue light.
Brain identifies red and green receptors to both be. There are three primary colours in light. Red green and blue.
But often we see different colours and patterns when we close our eyes in the dark. We see objects of different colors because light reflects. The physics of color perception involves energy wavelengths reflections and signals zapping back and forth in our.
The sensitivity of the eyes receptors to a light wavelength is responsible for color vision. When light from the banana hits the cones it stimulates them to varying degrees. Light receptors within the eye transmit messages to the brain which produces the familiar sensations of color.
The way we see colors isnt very straightforward. The primary colors of light are red green and blue which match up with the red green and blue-sensitve cone cells in the retinas of our. These light receptors are.
This dark yellow smeared over a wide portion of the spectrum is perceived as brown. Color is completely a phenomena of your eye. How do we see color chemistry.
A green object reflects green light. We perceive color as a result of light interacting with our eyes the. The resulting signal is zapped along the optic.
See second figure Fig. When you see objects you just receives light reflected or refracted from those objects which is perceived by your eye as color.

How We See Blue Color Infographic Diagram Showing Visible Spectrum Light On Surface And Colors Reflected Or Absorbed According To Its Color For Physics Science Education Royalty Free Svg Cliparts Vectors And

How Do We See Colors Reflection Of Colours Gcse Physics Youtube
The Physics Of Color Vision And Color Blindness What Is Color

Schrodinger Was Wrong New Research Overturns 100 Year Old Understanding Of Color Perception R Physics

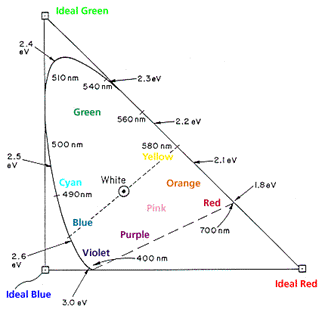
Wavelength To Colour Relationship Academo Org Free Interactive Education

Are Black And White Colors Light Pigments And Vision Reveal The Answer S Color Meanings
Optical Society Of America Exploring The Science Of Light Teachers And Parents Articles The Composition Of Color
![]()
Optics Color Icon Light Physics Branch Optometry Vector Image

Color Vision Photons Monochromatic Light White Light Phet Interactive Simulations
Optical Society Of America Exploring The Science Of Light Teachers And Parents Articles The Composition Of Color
Structural Color Manoharan Lab

Visible Light What Frequency Is Pink Color Physics Stack Exchange
Physics Tutorial Visible Light And The Eye S Response
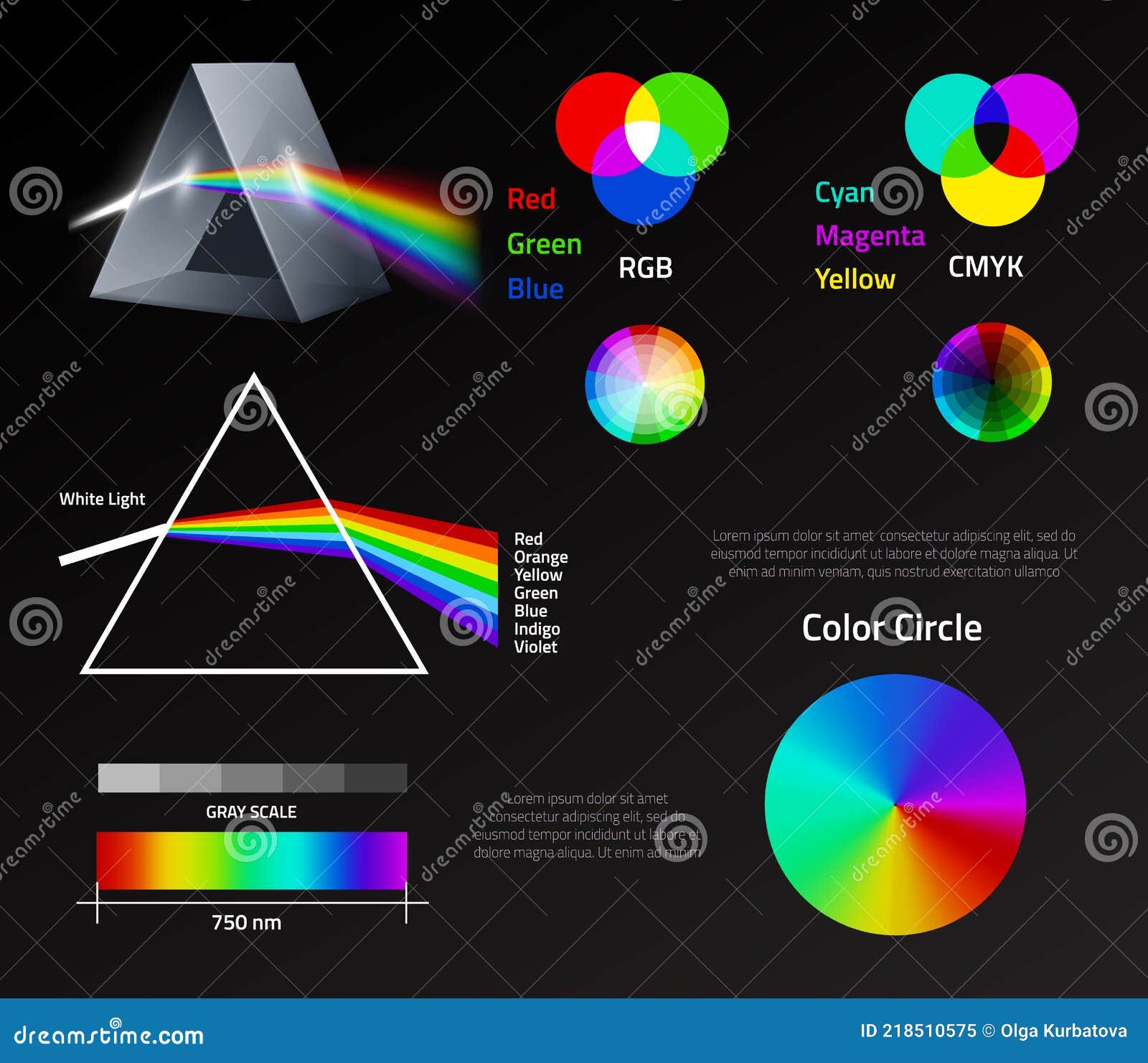
Light Prism Rainbow Spectrum Physics Refraction Color Circle Linear Schemes Visible Waves Color Rendering System Stock Vector Illustration Of Rainbow Dispersion 218510575

Conceptual Physics What Is Color Addition